How request and response travels on the internet
Guide on how request reaches the web server by traveling over the internet and how we receive a response
I was watching Netflix one day, and from somewhere one question Popped up in my mind,
Why browsers by mistake do not show facebook.com when entering netflix.com 🤔?
Also,
How the browser reaches the web server by only entering the Domain name?
and I'm sure you will be curious to know about it as well.
Let's, understand it from the below diagram,
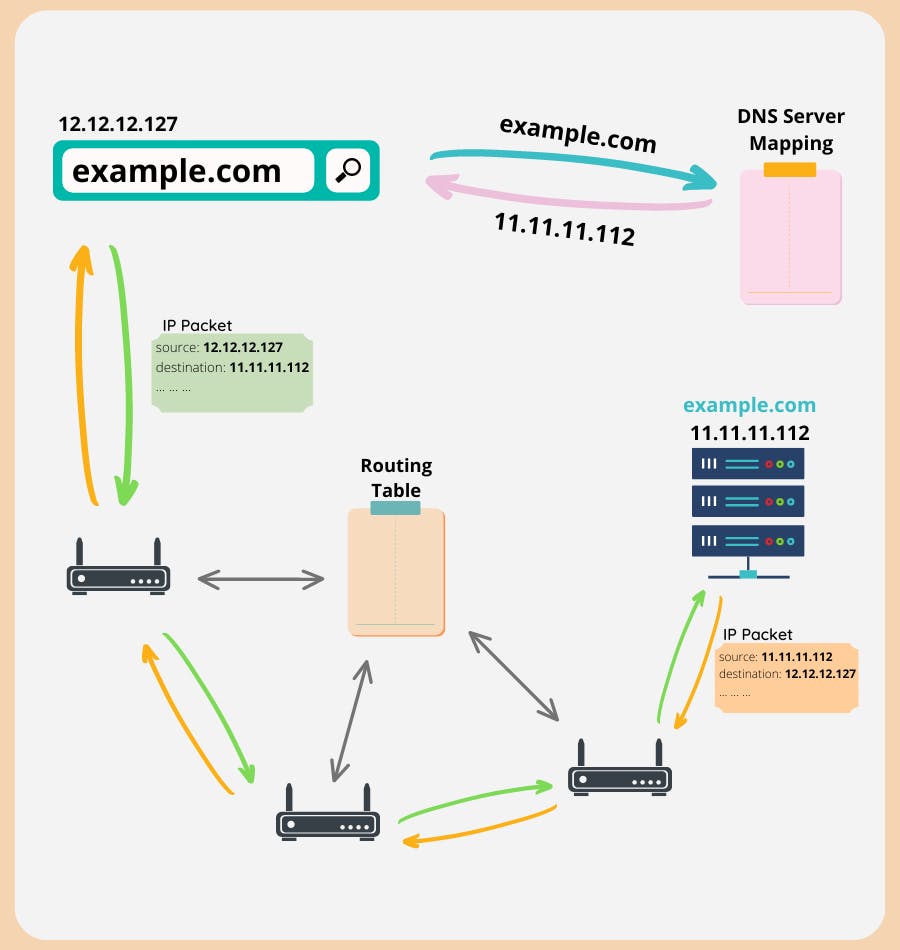
How does it work?
- The browser first makes a request to DNS Server to get IP Address for example.com, which is called DNS Lookup.
- Once IP Address is received, the Browser creates IP Packet for an HTTP request.
- IP Packet contains source, destination, and other information.
- IP Packet travels through default gateway of Internet provider and set of Routers.
- Based on the Routing table, Routers direct the Packet in the right direction towards the Web Server.
- The server extracts IP Packet, processes it, and returns the response.
- No DNS lookup is required to send the response, as the IP packet includes the computer's IP address as the source.
- The server sets the computer's address as the destination address in response and sends it.
Terminologies
Let's understand some of the terminologies explained here,
DNS Lookup
- Initially, Browser connects to DNS Serer to know the IP address of the domain name is known as DNS Lookup.
DNS Entry
- It refers to the mapping of Domain Name and IP Address stored as Table.
Domain Name Server
- It contains a List of DNS Entries. In most cases, it's provided by a Hosting service or organization like Google.
Domain Name System
- All Domain Name Servers share their entries with each other, which creates a Domain Name System.
IP Packet
- It gets created for HTTP Requests, It contains information like source address, destination address, body, etc pieces of information. One HTTP request may result in more than one IP packet.
Routers
- Routers are connected to more than one network.
- The Internet is a collection of interconnected networks.
- When the Router receives IP Packet, it looks in Routing Table and directs the IP Packet towards the Web Server.
Routing Table
- It refers to a set of rules, viewed as table format, that is used to determine where IP Packet traveling over the Internet will be directed.
This is all about the answer I got. I hope it gave light to your curiosity as well.
Thanks for reading and Let's connect, I'm available over LinkedIn and Twitter.
See you soon 👋.
